Medical imaging plays a vital role in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Among the most commonly used techniques are the MRI and ultrasound scans, each with unique capabilities and applications. Understanding these diagnostic tools can help patients feel more informed and comfortable.
What Is an MRI Scan?
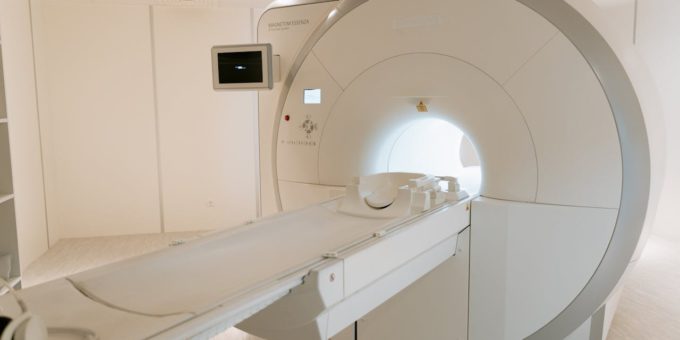
An MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI scans do not involve ionising radiation, making them a safer option for many patients.
How Does an MRI Scan Work?
During an MRI scan the strong magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body, and radio waves disrupt this alignment. As the atoms return to their original positions, they emit signals that a computer captures and translates into detailed images.
Common Uses of MRI Scans
MRI scans are particularly effective for imaging soft tissues, such as:
- Brain and Nervous System: Detecting tumours, multiple sclerosis, or stroke.
- Muscles and Joints: Diagnosing ligament tears, cartilage damage, or arthritis.
- Heart and Blood Vessels: Assessing heart function or detecting blockages.
- Abdomen and Pelvis: Identifying liver diseases, uterine abnormalities, or prostate issues.
The precision of MRI scans makes them invaluable in diagnosing and planning treatment for various conditions.
What to Expect During an MRI Scan
Patients undergoing an MRI scan should expect to lie still for 30 to 90 minutes, depending on the complexity of the scan. Some may feel claustrophobic inside the machine, but open MRI options are available at some facilities. Removing metal objects is essential, as the magnetic field can interact with them.
 What Is an Ultrasound Scan?
What Is an Ultrasound Scan?
An ultrasound scan, or sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the body’s internal structures. It is a widely used, non-invasive procedure that provides valuable insights without radiation.
How Does an Ultrasound Scan Work?
During an ultrasound scan, a technician applies a gel to the patient’s skin and moves a handheld device called a transducer over the examined area. The transducer emits sound waves, which bounce off internal structures and create echoes. These echoes are then processed to form visual images on a screen.
Common Uses of Ultrasound Scans
Ultrasound scans are versatile and frequently used in various medical fields, including:
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology: Monitoring fetal development during pregnancy.
- Cardiology: Assessing heart function with echocardiograms.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: Evaluating tendons, muscles, and joints.
Ultrasound scans are also used for guided procedures, such as biopsies or fluid drainage.
What to Expect During an Ultrasound Scan
Ultrasound scans are quick and painless and typically last between 15 and 45 minutes. Patients may need to adjust their position or hold their breath briefly to improve image quality. Unlike MRI scans, ultrasound scans are performed in real time, providing immediate results.
Comparing MRI and Ultrasound Scans
While MRI and ultrasound scans are essential diagnostic tools, they serve different purposes and excel in distinct areas.
Choosing the Right Imaging Technique
The choice between an MRI scan and an ultrasound scan depends on several factors, including the area of the body being examined, the specific condition being investigated, and the level of detail required. Physicians often recommend one technique over the other based on its suitability for the diagnosis.
For instance:
- An MRI scan is ideal for detecting complex issues like brain tumours, spinal cord injuries, or ligament tears.
- An ultrasound scan is the go-to option for monitoring pregnancy or assessing fluid-filled structures like the bladder.
Advancements in Imaging Technology
MRI and ultrasound technologies continue to evolve, offering enhanced imaging capabilities and improved patient comfort. For example, newer MRI machines are quieter and faster, reducing patient discomfort. Similarly, 3D and 4D ultrasound technologies provide more detailed and dynamic imaging, particularly obstetrics.
Preparing for Your Scan
Whether you’re scheduled for an MRI scan or an ultrasound scan, proper preparation can ensure the procedure goes smoothly:
- For MRI Scans: Wear loose, metal-free clothing and inform your doctor about any implants or medical devices.
- For Ultrasound Scans: Depending on the type of ultrasound, you may need to fast or drink water beforehand to fill your bladder.
MRI and ultrasound scans are indispensable tools in modern healthcare, each offering unique benefits for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions. Understanding how these technologies work and what to expect can alleviate anxiety and ensure a more comfortable experience. Whether undergoing an MRI scan for a detailed view of your internal structures or an ultrasound scan for real-time imaging, both techniques play a critical role in providing accurate and timely medical insights.